Riparian Health & Tree Planting
What is a Riparian Area?
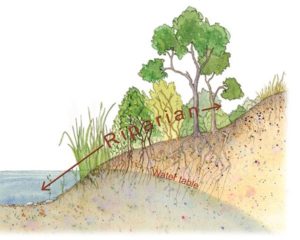
![]() Riparian areas are the green zones around surface water of a river, wetland or lake, that are the transitional area from the water’s edge to upland habitat.
Riparian areas are the green zones around surface water of a river, wetland or lake, that are the transitional area from the water’s edge to upland habitat.
![]() Riparian areas are formed as the result of water, soil, and vegetation interacting with one another
Riparian areas are formed as the result of water, soil, and vegetation interacting with one another
![]() Healthy riparian areas have abundant vegetation including, trees, shrubs, and herbaceous cover
Healthy riparian areas have abundant vegetation including, trees, shrubs, and herbaceous cover
 Functions of a Riparian Area
Functions of a Riparian Area
- Trap & Store Sediment
- Build & Maintain Banks & Shorelines
- Store Water & Energy
- Recharge Aquifers
- Filter & Buffer Water (EMS, SLCN)
- Reduce & Disperse Energy
- Act as animal travel corridors (EMS, SLCN)
- Maintain Biodiversity
- Create Primary Productivity
- Act as growing mediums for many traditional medicines that only grow in water or on the shores/banks of lakes and rivers (BLCN)
Importance of Trees and other Shoreline Vegetation
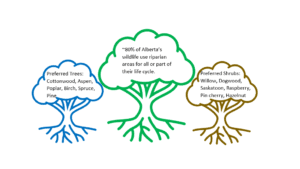
![]() Trees play a role in the uptake of nutrients that could otherwise degrade water quality
Trees play a role in the uptake of nutrients that could otherwise degrade water quality
![]() The canopies of trees and shrubs, protect the soil from erosion and provide shelter to wildlife
The canopies of trees and shrubs, protect the soil from erosion and provide shelter to wildlife
![]() Lakeside vegetation maintains the integrity and structure of the streambank
Lakeside vegetation maintains the integrity and structure of the streambank
![]() The vegetation resists erosion and traps sediment to build and restore the banks
The vegetation resists erosion and traps sediment to build and restore the banks
![]() Vegetation resists wave action and ice movement
Vegetation resists wave action and ice movement
![]() Root systems bind soil particles together and provide the glue that stabilizes the bank
Root systems bind soil particles together and provide the glue that stabilizes the bank
![]() When the deep binding roots of shrubs and trees are absent, shallow-rooted grasses cannot withstand erosion forces
When the deep binding roots of shrubs and trees are absent, shallow-rooted grasses cannot withstand erosion forces
![]() Riparian areas are used by many animals as travel corridors, they are abundant in foods for herbivores (SLCN, EMS)
Riparian areas are used by many animals as travel corridors, they are abundant in foods for herbivores (SLCN, EMS)
![]() These areas are critical habitat for several different species like semi-aquatic mammals, reptiles, amphibians, migratory birds, and other mammals (BLCN)
These areas are critical habitat for several different species like semi-aquatic mammals, reptiles, amphibians, migratory birds, and other mammals (BLCN)
![]() Some traditional medicines only grow in water or on the shores or banks of lakes/rivers (BLCN)
Some traditional medicines only grow in water or on the shores or banks of lakes/rivers (BLCN)



Jessie Lake Restoration (2020)
In 2021, LICA contracted Fiera Biological Consulting Ltd., to conduct Riparian Area Assessments in the Jackfish-Muriel Creeks Watershed, the Upper Beaver Watershed and on Reita Creek. The final reports can be found on the LICA Website, under the Watershed tab https://lica.ca/watershed/. Or click the links below to access the Final Reports directly.
The Riparian Area Assessment Summary of Results presentation recording, can be viewed below!
In addition to the Riparian Health Assessments noted above, LICA also contracted Cows & Fish to conduct riparian health inventories, on two sites located at Jessie Lake. A riparian health inventory is a tool designed to help evaluate and understand the health of riparian areas. These summary reports provide information on the current health of Jessie Lake taken at NW-12-61-6 W4 and SW 8-61-5 W4M. This information is intended to help direct efforts to promote important riparian functions such as improved water quality, forage production, and wildlife habitat.
Other Resources: Cows and Fish are a great resource for riparian area health, ecology, and function. Check out their ‘Caring for the Green Zone – Riparian Areas, a User’s Guide to Health’ booklet or visit their website at https://cowsandfish.org/
Developed in collaboration with: Beaver Lake Cree Nation (BLCN), Saddle Lake Cree Nation (SLCN), Elizabeth Métis Settlement (EMS) & Cows & Fish. Funding provided by Alberta Environment and Parks (AEP).